Analog Input Timing Summary
An acquisition with posttrigger data allows you to view data that is acquired after a trigger event is received. A typical posttrigger DAQ sequence is shown in the following figure. The sample counter is loaded with the specified number of posttrigger samples, in this example, five. The value decrements with each pulse on ai/SampleClock, until the value reaches zero and all desired samples have been acquired.
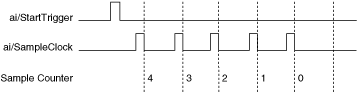
An acquisition with pretrigger data allows you to view data that is acquired before the trigger of interest, in addition to data acquired after the trigger. The following figure shows a typical pretrigger DAQ sequence. The ai/StartTrigger signal can be either a hardware or software signal. If ai/StartTrigger is set up to be a software start trigger, an output pulse appears on the AI START TRIG line when the acquisition begins. When the ai/StartTrigger pulse occurs, the sample counter is loaded with the number of pretrigger samples, in this example, four. The value decrements with each pulse on ai/SampleClock, until the value reaches zero. The sample counter is then loaded with the number of posttrigger samples, in this example, three.
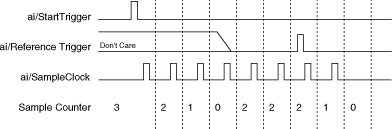
If an ai/ReferenceTrigger pulse occurs before the specified number of pretrigger samples are acquired, the trigger pulse is ignored. Otherwise, when the ai/ReferenceTrigger pulse occurs, the sample counter value decrements until the specified number of posttrigger samples have been acquired. For more information about start and reference triggers, refer to Analog Input Triggering.
In order to provide all of the timing functionality described throughout this section, the DAQ-STC provides an extremely powerful and flexible timing engine. For more information about all of the clock routing and timing options that the analog input timing engine provides, refer to the NI-DAQmx Help.

