Input Polarity and Range
Input range refers to the set of input voltages that an analog input channel can digitize with the specified accuracy. On some S Series devices, you can individually program the input range of each AI channel.
The input range affects the resolution of the S Series device for an AI channel. Resolution refers to the voltage of one ADC code. For example, a 16-bit ADC converts analog inputs into one of 65,536 (=216) codes, meaning one of 65,536 possible digital values. These values are spread fairly evenly across the input range. So, for an input range of –5 V to 5 V, the voltage of each code of a 16-bit ADC is:
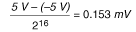
S Series devices support bipolar input ranges. A bipolar input range means that the input voltage range is between –Vref and Vref.
The instrumentation amplifier applies a different gain setting to the AI signal depending on the input range. Gain refers to the factor by which the instrumentation amplifier multiplies (amplifies) the input signal before sending it to the ADC.
On S Series devices with programmable input ranges, choose an input range that matches the expected input range of your signal. A large input range can accommodate a large signal variation, but reduces the voltage resolution. Choosing a smaller input range improves the voltage resolution, but may result in the input signal going out of range. For more information about programming these settings, refer to the NI-DAQmx Help.

